
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 011
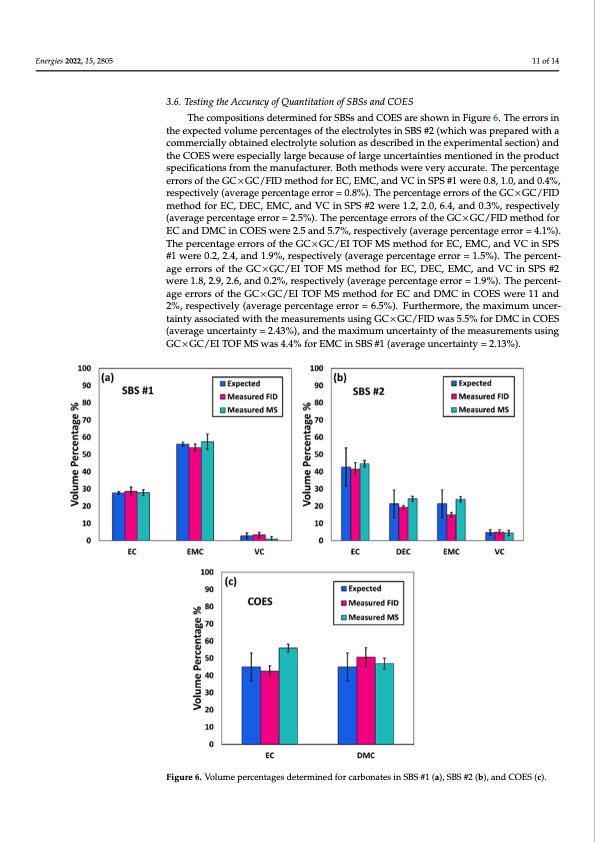
Energies 2022, 15, 2805 11 of 14 3.6. Testing the Accuracy of Quantitation of SBSs and COES The compositions determined for SBSs and COES are shown in Figure 6. The errors in the expected volume percentages of the electrolytes in SBS #2 (which was prepared with a commercially obtained electrolyte solution as described in the experimental section) and the COES were especially large because of large uncertainties mentioned in the product specifications from the manufacturer. Both methods were very accurate. The percentage errors of the GC×GC/FID method for EC, EMC, and VC in SPS #1 were 0.8, 1.0, and 0.4%, respectively (average percentage error = 0.8%). The percentage errors of the GC×GC/FID method for EC, DEC, EMC, and VC in SPS #2 were 1.2, 2.0, 6.4, and 0.3%, respectively (average percentage error = 2.5%). The percentage errors of the GC×GC/FID method for EC and DMC in COES were 2.5 and 5.7%, respectively (average percentage error = 4.1%). The percentage errors of the GC×GC/EI TOF MS method for EC, EMC, and VC in SPS #1 were 0.2, 2.4, and 1.9%, respectively (average percentage error = 1.5%). The percent- age errors of the GC×GC/EI TOF MS method for EC, DEC, EMC, and VC in SPS #2 were 1.8, 2.9, 2.6, and 0.2%, respectively (average percentage error = 1.9%). The percent- age errors of the GC×GC/EI TOF MS method for EC and DMC in COES were 11 and 2%, respectively (average percentage error = 6.5%). Furthermore, the maximum uncer- tainty associated with the measurements using GC×GC/FID was 5.5% for DMC in COES Energies 2022, 15, x FOR PEER REVIEW 12 of 14 (average uncertainty = 2.43%), and the maximum uncertainty of the measurements using GC×GC/EI TOF MS was 4.4% for EMC in SBS #1 (average uncertainty = 2.13%). Figure 6. Volume percentages determined for carbonates in SBS #1 (a), SBS #2 (b), and COES (c). Figure 6. Volume percentages determined for carbonates in SBS #1 (a), SBS #2 (b), and COES (c).PDF Image | Carbonate Solvent Systems Used in Lithium-Ion Batteries
PDF Search Title:
Carbonate Solvent Systems Used in Lithium-Ion BatteriesOriginal File Name Searched:
energies-15-02805.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Product and Development Focus for Infinity Turbine
ORC Waste Heat Turbine and ORC System Build Plans: All turbine plans are $10,000 each. This allows you to build a system and then consider licensing for production after you have completed and tested a unit.Redox Flow Battery Technology: With the advent of the new USA tax credits for producing and selling batteries ($35/kW) we are focussing on a simple flow battery using shipping containers as the modular electrolyte storage units with tax credits up to $140,000 per system. Our main focus is on the salt battery. This battery can be used for both thermal and electrical storage applications. We call it the Cogeneration Battery or Cogen Battery. One project is converting salt (brine) based water conditioners to simultaneously produce power. In addition, there are many opportunities to extract Lithium from brine (salt lakes, groundwater, and producer water).Salt water or brine are huge sources for lithium. Most of the worlds lithium is acquired from a brine source. It's even in seawater in a low concentration. Brine is also a byproduct of huge powerplants, which can now use that as an electrolyte and a huge flow battery (which allows storage at the source).We welcome any business and equipment inquiries, as well as licensing our turbines for manufacturing.| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |