
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 013
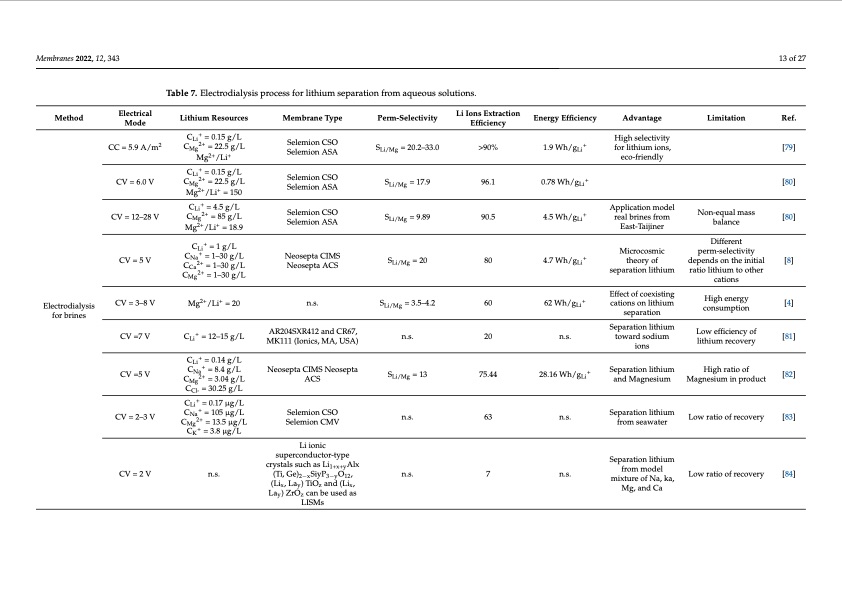
Membranes 2022, 12, 343 13 of 27 Ref. [79] [80] [80] [8] [4] [81] [82] [83] [84] Table 7. Electrodialysis process for lithium separation from aqueous solutions. Method Electrical Mode CC = 5.9 A/m2 CV = 6.0 V CV = 12–28 V CV=5V CV = 3–8 V Lithium Resources CLi+ = 0.15 g/L CMg2+ = 22.5 g/L Mg2+/Li+ CLi+ = 0.15 g/L CMg2+ = 22.5 g/L Mg2+/Li+ = 150 CLi+ = 4.5 g/L CMg2+ = 85 g/L Mg2+/Li+ = 18.9 CLi+ = 1 g/L C + = 1–30 g/L Na CCa2+ = 1–30 g/L CMg2+ = 1–30 g/L Mg2+/Li+ = 20 Membrane Type Selemion CSO Selemion ASA Selemion CSO Selemion ASA Selemion CSO Selemion ASA Neosepta CIMS Neosepta ACS n.s. AR204SXR412 and CR67, MK111 (Ionics, MA, USA) Neosepta CIMS Neosepta ACS Selemion CSO Selemion CMV Li ionic superconductor-type crystals such as Li1+x+yAlx (Ti, Ge)2−xSiyP3−yO12, (Lix, Lay) TiOz and (Lix, Lay) ZrOz can be used as LISMs Perm-Selectivity SLi/Mg = 20.2–33.0 SLi/Mg = 17.9 SLi/Mg = 9.89 Li Ions Extraction Efficiency >90% 96.1 90.5 80 60 20 75.44 63 7 Energy Efficiency 1.9 Wh/gLi+ 0.78 Wh/gLi+ 4.5 Wh/gLi+ 4.7Wh/g + Li 62 Wh/gLi+ n.s. 28.16 Wh/g + Li n.s. n.s. Advantage High selectivity for lithium ions, eco-friendly Application model real brines from East-Taijiner Microcosmic theoryof separation lithium Effect of coexisting cations on lithium separation Separation lithium toward sodium ions Separation lithium and Magnesium Separation lithium from seawater Separation lithium from model mixture of Na, ka, Mg, and Ca Limitation S Li/Mg =20 Non-equal mass balance Different perm-selectivity dependsontheinitial ratio lithium to other cations High energy consumption Low efficiency of lithium recovery High ratio of Magnesium in product Low ratio of recovery Low ratio of recovery Electrodialysis for brines SLi/Mg = 3.5–4.2 n.s. CV =7 V CLi + = 12–15 g/L CV =5 V CV = 2–3 V CV = 2 V CLi+ = 0.14 g/L CNa+ = 8.4 g/L CMg2+ = 3.04 g/L CCl- = 30.25 g/L CLi+ = 0.17 μg/L CNa+ = 105 μg/L CMg2+ = 13.5 μg/L CK+ = 3.8 μg/L n.s. S Li/Mg = 13 n.s. n.s.PDF Image | Electro-Driven Materials and Processes for Lithium
PDF Search Title:
Electro-Driven Materials and Processes for LithiumOriginal File Name Searched:
membranes-12-00343-v3.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Product and Development Focus for Infinity Turbine
ORC Waste Heat Turbine and ORC System Build Plans: All turbine plans are $10,000 each. This allows you to build a system and then consider licensing for production after you have completed and tested a unit.Redox Flow Battery Technology: With the advent of the new USA tax credits for producing and selling batteries ($35/kW) we are focussing on a simple flow battery using shipping containers as the modular electrolyte storage units with tax credits up to $140,000 per system. Our main focus is on the salt battery. This battery can be used for both thermal and electrical storage applications. We call it the Cogeneration Battery or Cogen Battery. One project is converting salt (brine) based water conditioners to simultaneously produce power. In addition, there are many opportunities to extract Lithium from brine (salt lakes, groundwater, and producer water).Salt water or brine are huge sources for lithium. Most of the worlds lithium is acquired from a brine source. It's even in seawater in a low concentration. Brine is also a byproduct of huge powerplants, which can now use that as an electrolyte and a huge flow battery (which allows storage at the source).We welcome any business and equipment inquiries, as well as licensing our turbines for manufacturing.| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |