
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 013
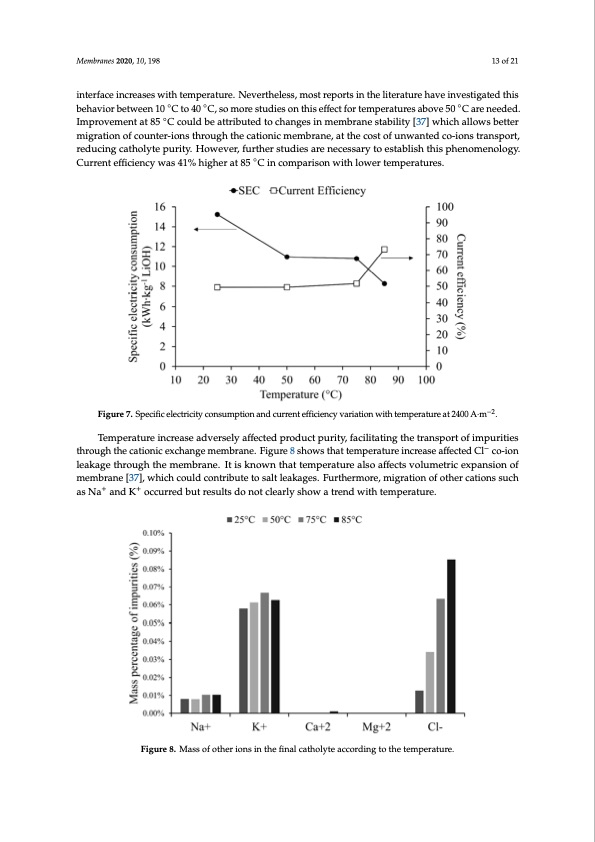
Membranes 2020, 10, x FOR PEER REVIEW 13 of 22 membrane surface and it can also affect membrane conductivity and volumetric expansion [37]. A Membranes 2020, 10, 198 slight variation in SEC between 50 °C and 75 °C was observed. For this, two explanations were proposed, first, a non-linear variation between temperature and conductivity of the electrolyte, and 13 of 21 second, electrical resistance variations in cell components. Here, the cationic membrane may have interface inmcorreaisneflsuwenictehthteamn bpuelkrastoulurtei.onNaenvdebrothunedleasrys,lmayoerst[r3e8p–4o0r].tsItiins kthneowlintetrhatutraenshpaovrtetihnrovuegshtigated this membrane–el◦ectrolyte ◦interface increases with temperature. Nevertheless, most reports in◦the behaviorbetween10 Cto40 C,somorestudiesonthiseffectfortemperaturesabove50 Careneeded. literature have investigated this behavior between 10 °C to 40 °C, so more studies on this effect for Improvement at 85 ◦C could be attributed to changes in membrane stability [37] which allows better temperatures above 50 °C are needed. Improvement at 85 °C could be attributed to changes in migration of counter-ions through the cationic membrane, at the cost of unwanted co-ions transport, membrane stability [37] which allows better migration of counter-ions through the cationic reducing cmaetmhobrlaynte, patuthrietyco.sHt oofwunewvaenrt,efducrot-hioenrssttruandspieosrta, rednuceicnegscsaathroylyttoe epsutraitby.liHshowtehviesr,pfhurethneormenology. studies are necessary to establish this ◦phenomenology. Current efficiency was 41% higher at 85 °C in Current efficiency was 41% higher at 85 C in comparison with lower temperatures. comparison with lower temperatures. Figure 7. Specific electricity consumption and current efficiency variation with temperature at 2400 A·m−2. Figure 7. Specific electricity consumption and current efficiency variation with temperature at 2400 A∙m−2. Temperature increase adversely affected product purity, facilitating the transport of impurities throughthecaTtieomnpiecraetxucrheaincgreasmeeadmvbersaenlyea.ffFeicgteudrepr8odsuhcotwpusritthya,ftatceilmitaptienrgatthuerterainscproeratsoefiamffpeucrtietidesCl−co-ion through the cationic exchange membrane. Figure 8 shows that temperature increase affected Cl− co- leakage through the membrane. It is known that temperature also affects volumetric expansion of ion leakage through the membrane. It is known that temperature also affects volumetric expansion membrane [37], which could contribute to salt leakages. Furthermore, migration of other cations such as Na ++ of membrane [37], which could contribute to salt leakages. Furthermore, migration of other cations bRuPtEErReRsEuVlItEsWdo not clearly show a trend with temperature. 14 of 22 With respect to energy parameters in the membrane electrodialysis cell, the best result was obtained at 85 °C. Related to product purity, it is clear that low temperature reduced salt leakages through the membrane. Figure 8. Mass of other ions in the final catholyte according to the temperature. Figure 8. Mass of other ions in the final catholyte according to the temperature. 4.3. Membrane Type Influence The effect of ion exchange membrane type on product purity can be observed when experiments 2 and 6 are compared. When using Nafion 115 and Nafion 117 membranes, purity percentages of 94.03% and 98.17% were obtained in lithium hydroxide monohydrate crystals, respectively. Other results such as production rate, cell voltage, current efficiency and specific electrical consumption did not present significant differences according to the membrane type used. +, 1r0r,exdFO+ anMdemKbraneso2c0c20u such as Na and K occurred but results do not clearly show a trend with temperature. In all results with both membranes, chemical analysis indicated the presence of other cationsPDF Image | Battery Grade Li Hydroxide by Membrane Electrodialysis
PDF Search Title:
Battery Grade Li Hydroxide by Membrane ElectrodialysisOriginal File Name Searched:
membranes-10-00198.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Product and Development Focus for Infinity Turbine
ORC Waste Heat Turbine and ORC System Build Plans: All turbine plans are $10,000 each. This allows you to build a system and then consider licensing for production after you have completed and tested a unit.Redox Flow Battery Technology: With the advent of the new USA tax credits for producing and selling batteries ($35/kW) we are focussing on a simple flow battery using shipping containers as the modular electrolyte storage units with tax credits up to $140,000 per system. Our main focus is on the salt battery. This battery can be used for both thermal and electrical storage applications. We call it the Cogeneration Battery or Cogen Battery. One project is converting salt (brine) based water conditioners to simultaneously produce power. In addition, there are many opportunities to extract Lithium from brine (salt lakes, groundwater, and producer water).Salt water or brine are huge sources for lithium. Most of the worlds lithium is acquired from a brine source. It's even in seawater in a low concentration. Brine is also a byproduct of huge powerplants, which can now use that as an electrolyte and a huge flow battery (which allows storage at the source).We welcome any business and equipment inquiries, as well as licensing our turbines for manufacturing.| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |