
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 003
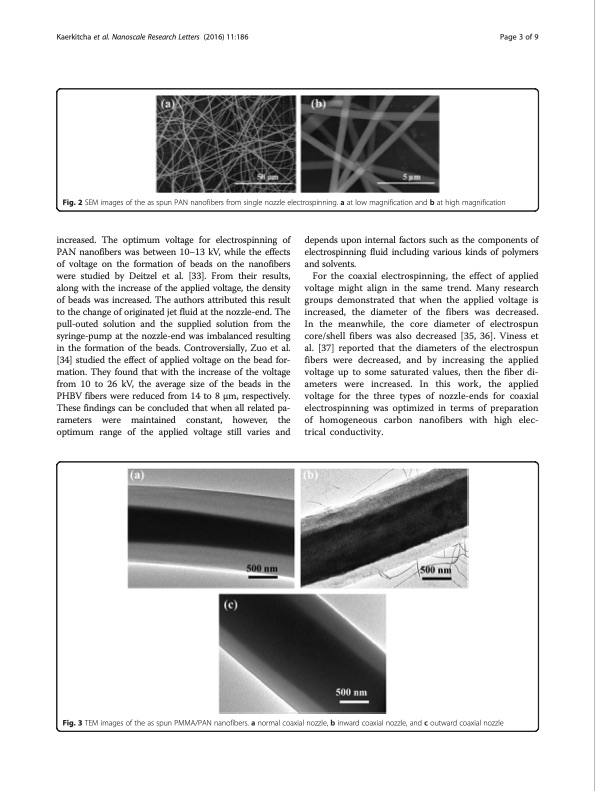
Kaerkitcha et al. Nanoscale Research Letters (2016) 11:186 Page 3 of 9 Fig. 2 SEM images of the as spun PAN nanofibers from single nozzle electrospinning. a at low magnification and b at high magnification increased. The optimum voltage for electrospinning of PAN nanofibers was between 10–13 kV, while the effects of voltage on the formation of beads on the nanofibers were studied by Deitzel et al. [33]. From their results, along with the increase of the applied voltage, the density of beads was increased. The authors attributed this result to the change of originated jet fluid at the nozzle-end. The pull-outed solution and the supplied solution from the syringe-pump at the nozzle-end was imbalanced resulting in the formation of the beads. Controversially, Zuo et al. [34] studied the effect of applied voltage on the bead for- mation. They found that with the increase of the voltage from 10 to 26 kV, the average size of the beads in the PHBV fibers were reduced from 14 to 8 μm, respectively. These findings can be concluded that when all related pa- rameters were maintained constant, however, the optimum range of the applied voltage still varies and depends upon internal factors such as the components of electrospinning fluid including various kinds of polymers and solvents. For the coaxial electrospinning, the effect of applied voltage might align in the same trend. Many research groups demonstrated that when the applied voltage is increased, the diameter of the fibers was decreased. In the meanwhile, the core diameter of electrospun core/shell fibers was also decreased [35, 36]. Viness et al. [37] reported that the diameters of the electrospun fibers were decreased, and by increasing the applied voltage up to some saturated values, then the fiber di- ameters were increased. In this work, the applied voltage for the three types of nozzle-ends for coaxial electrospinning was optimized in terms of preparation of homogeneous carbon nanofibers with high elec- trical conductivity. Fig. 3 TEM images of the as spun PMMA/PAN nanofibers. a normal coaxial nozzle, b inward coaxial nozzle, and c outward coaxial nozzlePDF Image | carbon nanofibers obtained from coaxial electrospinning
PDF Search Title:
carbon nanofibers obtained from coaxial electrospinningOriginal File Name Searched:
s11671-016-1416-7.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |