PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 063
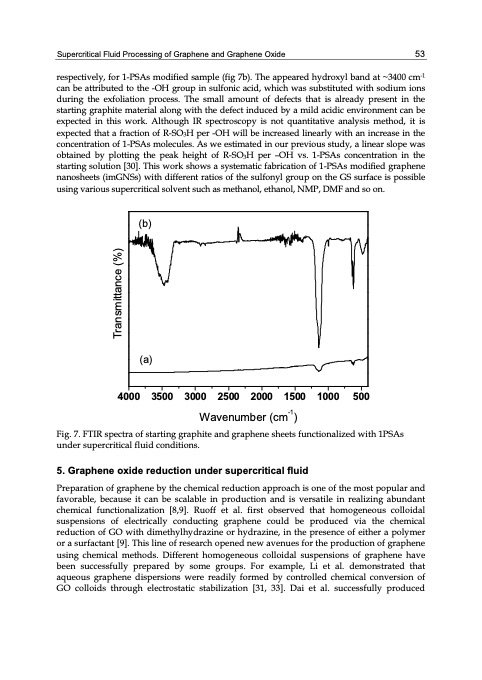
Supercritical Fluid Processing of Graphene and Graphene Oxide 53 respectively, for 1-PSAs modified sample (fig 7b). The appeared hydroxyl band at ~3400 cm-1 can be attributed to the -OH group in sulfonic acid, which was substituted with sodium ions during the exfoliation process. The small amount of defects that is already present in the starting graphite material along with the defect induced by a mild acidic environment can be expected in this work. Although IR spectroscopy is not quantitative analysis method, it is expected that a fraction of R-SO3H per -OH will be increased linearly with an increase in the concentration of 1-PSAs molecules. As we estimated in our previous study, a linear slope was obtained by plotting the peak height of R-SO3H per –OH vs. 1-PSAs concentration in the starting solution [30]. This work shows a systematic fabrication of 1-PSAs modified graphene nanosheets (imGNSs) with different ratios of the sulfonyl group on the GS surface is possible using various supercritical solvent such as methanol, ethanol, NMP, DMF and so on. (b) (a) 4000 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Wavenumber (cm-1) Fig. 7. FTIR spectra of starting graphite and graphene sheets functionalized with 1PSAs under supercritical fluid conditions. 5. Graphene oxide reduction under supercritical fluid Preparation of graphene by the chemical reduction approach is one of the most popular and favorable, because it can be scalable in production and is versatile in realizing abundant chemical functionalization [8,9]. Ruoff et al. first observed that homogeneous colloidal suspensions of electrically conducting graphene could be produced via the chemical reduction of GO with dimethylhydrazine or hydrazine, in the presence of either a polymer or a surfactant [9]. This line of research opened new avenues for the production of graphene using chemical methods. Different homogeneous colloidal suspensions of graphene have been successfully prepared by some groups. For example, Li et al. demonstrated that aqueous graphene dispersions were readily formed by controlled chemical conversion of GO colloids through electrostatic stabilization [31, 33]. Dai et al. successfully produced Transmittance (%)PDF Image | GRAPHENE SYNTHESIS CHARACTERIZATION PROPERTIES
PDF Search Title:
GRAPHENE SYNTHESIS CHARACTERIZATION PROPERTIESOriginal File Name Searched:
Graphene-Synthesis.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Salgenx Redox Flow Battery Technology: Power up your energy storage game with Salgenx Salt Water Battery. With its advanced technology, the flow battery provides reliable, scalable, and sustainable energy storage for utility-scale projects. Upgrade to a Salgenx flow battery today and take control of your energy future.
CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com (Standard Web Page)