
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 290
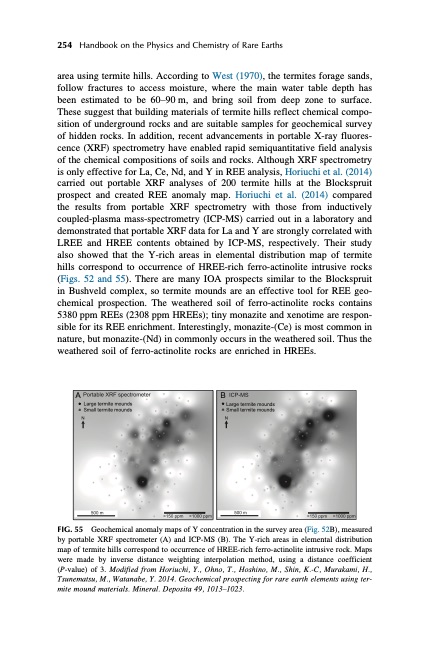
254 Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths area using termite hills. According to West (1970), the termites forage sands, follow fractures to access moisture, where the main water table depth has been estimated to be 60–90 m, and bring soil from deep zone to surface. These suggest that building materials of termite hills reflect chemical compo- sition of underground rocks and are suitable samples for geochemical survey of hidden rocks. In addition, recent advancements in portable X-ray fluores- cence (XRF) spectrometry have enabled rapid semiquantitative field analysis of the chemical compositions of soils and rocks. Although XRF spectrometry is only effective for La, Ce, Nd, and Y in REE analysis, Horiuchi et al. (2014) carried out portable XRF analyses of 200 termite hills at the Blockspruit prospect and created REE anomaly map. Horiuchi et al. (2014) compared the results from portable XRF spectrometry with those from inductively coupled-plasma mass-spectrometry (ICP-MS) carried out in a laboratory and demonstrated that portable XRF data for La and Y are strongly correlated with LREE and HREE contents obtained by ICP-MS, respectively. Their study also showed that the Y-rich areas in elemental distribution map of termite hills correspond to occurrence of HREE-rich ferro-actinolite intrusive rocks (Figs. 52 and 55). There are many IOA prospects similar to the Blockspruit in Bushveld complex, so termite mounds are an effective tool for REE geo- chemical prospection. The weathered soil of ferro-actinolite rocks contains 5380 ppm REEs (2308 ppm HREEs); tiny monazite and xenotime are respon- sible for its REE enrichment. Interestingly, monazite-(Ce) is most common in nature, but monazite-(Nd) in commonly occurs in the weathered soil. Thus the weathered soil of ferro-actinolite rocks are enriched in HREEs. FIG. 55 Geochemical anomaly maps of Y concentration in the survey area (Fig. 52B), measured by portable XRF spectrometer (A) and ICP-MS (B). The Y-rich areas in elemental distribution map of termite hills correspond to occurrence of HREE-rich ferro-actinolite intrusive rock. Maps were made by inverse distance weighting interpolation method, using a distance coefficient (P-value) of 3. Modified from Horiuchi, Y., Ohno, T., Hoshino, M., Shin, K.-C, Murakami, H., Tsunematsu, M., Watanabe, Y. 2014. Geochemical prospecting for rare earth elements using ter- mite mound materials. Mineral. Deposita 49, 1013–1023. A Large termite mounds Small termite mounds N B N Large termite mounds Small termite moundsPDF Image | HANDBOOK ON THE PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY OF RARE EARTHS
PDF Search Title:
HANDBOOK ON THE PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY OF RARE EARTHSOriginal File Name Searched:
Chemistry-Rare-Earths-49.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |