
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 224
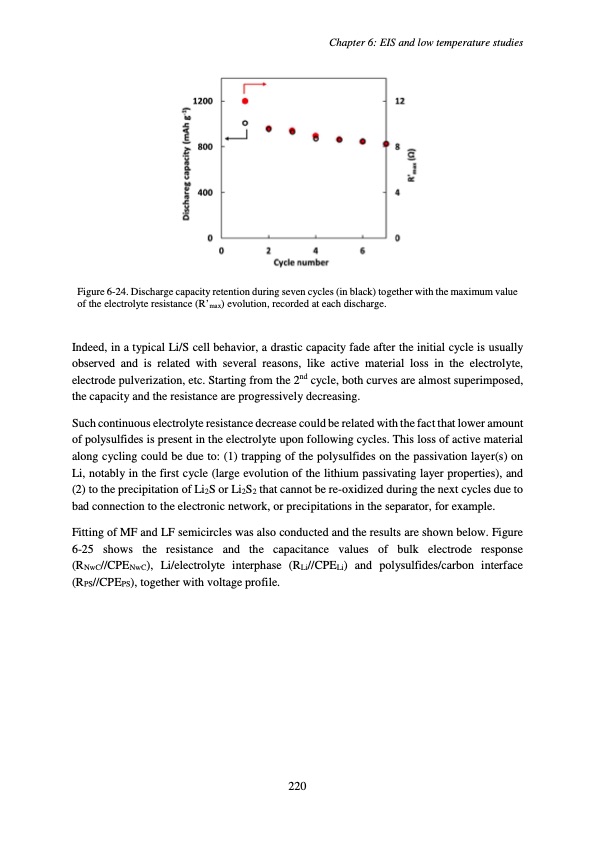
Figure 6-24. Discharge capacity retention during seven cycles (in black) together with the maximum value of the electrolyte resistance (R’max) evolution, recorded at each discharge. Indeed, in a typical Li/S cell behavior, a drastic capacity fade after the initial cycle is usually observed and is related with several reasons, like active material loss in the electrolyte, electrode pulverization, etc. Starting from the 2nd cycle, both curves are almost superimposed, the capacity and the resistance are progressively decreasing. Such continuous electrolyte resistance decrease could be related with the fact that lower amount of polysulfides is present in the electrolyte upon following cycles. This loss of active material along cycling could be due to: (1) trapping of the polysulfides on the passivation layer(s) on Li, notably in the first cycle (large evolution of the lithium passivating layer properties), and (2) to the precipitation of Li2S or Li2S2 that cannot be re-oxidized during the next cycles due to bad connection to the electronic network, or precipitations in the separator, for example. Fitting of MF and LF semicircles was also conducted and the results are shown below. Figure 6-25 shows the resistance and the capacitance values of bulk electrode response (RNwC//CPENwC), Li/electrolyte interphase (RLi//CPELi) and polysulfides/carbon interface (RPS//CPEPS), together with voltage profile. 220 Chapter 6: EIS and low temperature studiesPDF Image | Accumulateur Lithium Soufre
PDF Search Title:
Accumulateur Lithium SoufreOriginal File Name Searched:
WALUS_2015_archivage.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2 Sulfur Deposition on Carbon Nanofibers using Supercritical CO2. Gamma sulfur also known as mother of pearl sulfur and nacreous sulfur... More Info
CO2 Organic Rankine Cycle Experimenter Platform The supercritical CO2 phase change system is both a heat pump and organic rankine cycle which can be used for those purposes and as a supercritical extractor for advanced subcritical and supercritical extraction technology. Uses include producing nanoparticles, precious metal CO2 extraction, lithium battery recycling, and other applications... More Info
| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@infinityturbine.com | RSS | AMP |